Before we talk about how we can make electricity from sunlight, let’s talk about what these two things actually are…
What is sunlight?
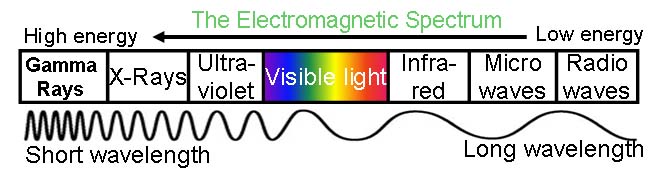
The sun emits what we call electromagnetic radiation which can be divided up into seven regions: radio waves, microwaves, infra-red radiation, visible light, ultra-violet light, x-rays and gamma radiation. This is known as the electromagnetic spectrum.
You have probably heard of some of these regions as we use many of them everyday. Microwaves are used in microwave ovens to give energy to the water in your food to warm it up. We use infra-red radiation in our TV remote controls.
If you look through your mobile phone camera at the infra-red emitter on the front of your remote-controls you will see flashing when you push the buttons. You do not see this without the phone. The mobile phone camera is able to pick up electromagnetic radiation at a slightly lower energy than your eyes can. Infra-red radiation also interacts with your body in a way that we call heat.
Technically the whole spectrum could be called sunlight, but what you would probably think of sunlight is the visible light region, the part of the spectrum that allows us to see things and gives objects colour.
We are protected from a lot of the harmful parts of the electromagnetic radiation by Earth’s atmosphere. Astrophysicists want to study some of this electromagnetic radiation coming from other stars and galaxies. They have to send satellites up into space to get above our absorbing atmosphere. However, some ultra-violet light can get through and causes sunburn if we are in the sun for too long without suncream.
The visible and infra-red regions of the spectrum are what our sun produces the most of. Therefore, it is important for people designing solar cells to try and capture these regions in order to make electricity and usually scientists concentrate on absorbing the visible region.
The visible region can be split up into the colours of the rainbow. You see a rainbow when visible sunlight is split into its colours by water in the air.
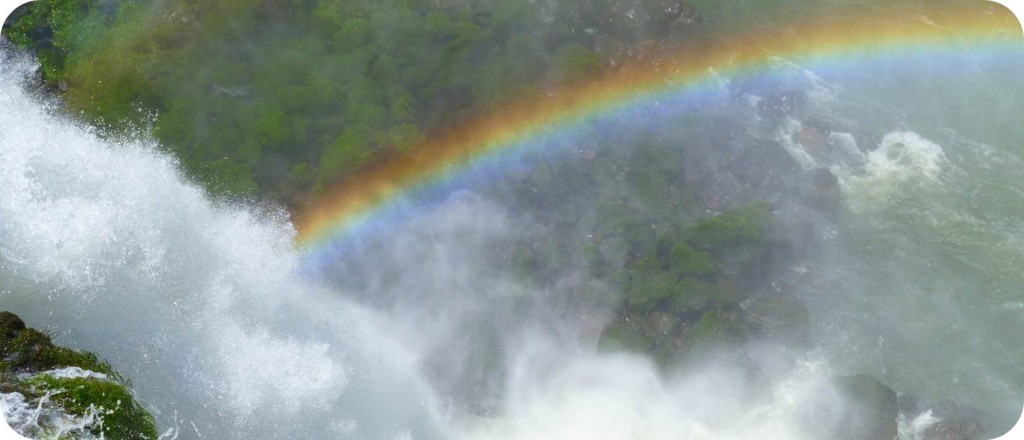

Ever notice that you often see a rainbow when there’s sun and water about? That because the water droplets split the sunlight into its colours.
What is electricity?
Electricity is the flow of electric charge through a circuit. Electric charge is a property of particles. Protons have a positive charge and electrons have a negative charge. Protons and electrons are the particles that make up atoms.
Electricity is often made by making an atom give up one of the negative electrons inside it, leaving the atom with a overall positive charge. This atom is now called a positive ion. Once the electron is released, it is conducted away from the ion and flows around a circuit like an electric wire, thus electricity is produced.
To generate electricity, it is important to separate the negative and positive charges so that a flow of electric charge is created. This flow then be used to do work on a system, such as power an electrical device.
How can sunlight make electricity?
The photoelectric effect was first observed in 1887. This effect is where the absorption of sunlight by a material causes the material to emit electrons. The sunlight absorbed is usually in the visible or ultra-violet region of the electromagnetic spectrum.
This phenomenon is where solar power all started. The ability of the sun’s energy to separate an electron from an atom in this material is the first step to making electricity. The electron can be separated from the now positively charged atom (ion). Once we have this charge separation, we can bring about a flow of electric charge through a circuit and this is our electricity.
Explore the pages below to find out about different types of technology which make use of this phenomenon!